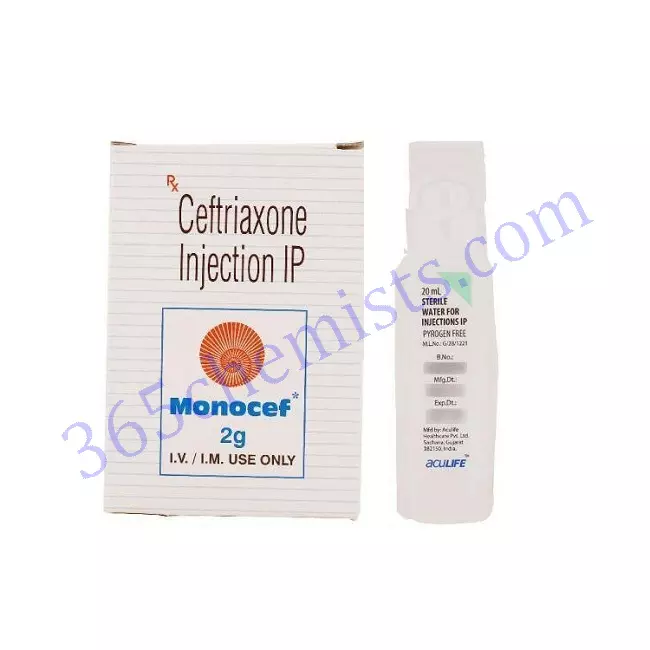
Monocef 2gm Injection: Potent Ceftriaxone Treatment for Severe Bacterial Infections
Ceftriaxone 2gm is the powerful active component of the medication known as Monocef 2gm Injection, which is a potent medication. Ceftriaxone is a cephalosporin antibiotic with a wide spectrum of activity that is well-known for its effectiveness in the treatment of severe bacterial infections. If you are struggling with an infection of the respiratory tract, an infection of the urinary tract, an infection of the skin and soft tissues, or any other type of infection that is complicated, Monocef 2gm Injection is a reliable solution that can combat bacterial pathogens and help promote recovery.
Potent Antibacterial Action
By preventing the production of bacterial cell walls, ceftriaxone, the primary ingredient in Monocef 2gm Injection, is able to produce the powerful antibacterial effect that the medication is known for. Ceftriaxone causes the death of bacteria by interfering with their ability to form cell walls. It does this by binding to certain proteins in the bacterial cell wall that are known as penicillin-binding proteins. Ceftriaxone is able to effectively fight off a wide variety of bacteria thanks to the mechanism of action that it employs. Some of these bacteria include Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, Escherichia coli, and Neisseria gonorrhoeae. These bacterial pathogens are targeted by the Monocef 2gm Injection, which controls the infection and alleviates the symptoms that are associated with it.
Versatile Treatment Options
Because it is effective against such a wide variety of bacterial strains, Monocef 2gm Injection can be used in a variety of different treatment scenarios. It is frequently recommended for patients suffering from severe infections of the respiratory tract, such as pneumonia and empyema, as well as complicated infections of the urinary tract, such as pyelonephritis and prostatitis. In addition to this, the Monocef 2gm Injection is useful for treating complicated skin and soft tissue infections that are brought on by bacteria that are susceptible to the medication. Because of its versatility, Monocef 2gm Injection is an instrument that is absolutely necessary for medical professionals to have when they are treating severe bacterial infections.
Related Dosage
Monocef O 100mg DT Tablet
Monocef O 100mg Tablet
Monocef O 200mg Tablet
Monocef O 50mg Oral Suspension
Monocef O 100mg Oral Suspension
Monocef O CV DT Tablet
Monocef O Kid 50mg Tablet
Monocef 1gm Injection
Monocef 2gm Injection
Monocef 125mg Injection
Monocef 250mg Injection
Monocef 500mg Injection
Monocef SB 1g Injection
Dosage and Administration
The appropriate dosage of Monocef 2gm Injection will be established by a medical professional with consideration given to the nature and extent of the infection, as well as the age, weight, and kidney function of the individual being treated. Intravenous administration under the direction of a qualified medical professional is the typical method of administration. It is possible for the dosage, frequency, and length of treatment to change depending on the particular infection being treated as well as the patient’s reaction to the medication. It is extremely important to take the medication exactly as directed by the healthcare provider, including in terms of the dosage and how it should be administered.
Safety and Monitoring
Even though Monocef 2gm Injection is generally safe and well tolerated, it is still important to take all necessary safety precautions. Because ceftriaxone has the potential to cause kidney problems in some people, it is imperative that their renal function be monitored on a regular basis. Tests of renal function might be done in order to make sure that the dosage is adjusted appropriately if that turns out to be necessary. Before beginning treatment with Monocef 2gm Injection, it is essential to provide the healthcare provider with information regarding any pre-existing medical conditions, medications that are currently being taken, or known allergies. The medical professional will evaluate whether or not the medication is appropriate for the patient, and they will carefully watch the patient for any negative side effects.
Preventing Antibiotic Resistance
The prudent administration of Monocef 2gm Injection is absolutely necessary in order to forestall the development of antibiotic resistance. It should only be used when absolutely necessary and for the amount of time that is specified. Antibiotics should not be used inappropriately or in excess, as this helps to preserve their effectiveness and ensures that they continue to be effective in the fight against severe bacterial infections. If you have any concerns or questions about the correct use of Monocef 2gm Injection, you should discuss them with your healthcare provider so that they can direct you.
Conclusion
A highly potent medication that is used for the treatment of severe bacterial infections, Monocef 2gm Injection contains 2gm of ceftriaxone and is available as an injection. Because of its broad-spectrum activity, versatility, and efficacy, it is a trusted choice among medical professionals for the management of complicated skin and soft tissue infections, deep-seated urinary tract infections, and respiratory tract infections. Monocef 2gm Injection is able to effectively control severe infections, alleviate symptoms, and promote recovery when the prescribed dosage is followed, safety precautions are adhered to, and consultation with a healthcare provider is sought. It is recommended that you speak with your healthcare provider if you have any questions or concerns regarding the use of Monocef 2gm Injection. Your healthcare provider can provide you with individualised guidance and information. With the help of Monocef 2gm Injection, you will receive effective treatment and be able to restore your health.